10 Questions Every Industrial Business Owner Should Ask Before Spending Another Dollar on Marketing
Posted by Greg Frye
How Feedback Shapes Strategy
Posted by Greg Frye
The Power of AI-Driven Content Development for Industrial Businesses
Posted by Greg Frye
Making Better Plans for Marketing: Lessons from Seth Godin’s This is Strategy
Posted by Eric Frye
How Industrial Businesses Can Use Content Marketing to Drive Growth
Posted by Eric Frye
The Industrial Business Owner’s Guide to Effective Email Marketing
Posted by Erin Meyer
Does Your Industrial Business Need a Stronger Marketing Strategy?
Posted by Eric Frye
How Industrial Businesses Can Build Trust and Strengthen Customer Relationships
Posted by Greg Frye
Marketing in 2025: A Strategy-First Approach for Industrial Business Owners
Posted by Eric Frye
Upright Communications Welcomes Stone Antoun to the Team
Posted by Upright Team
Best Marketing Strategies for Industrial Manufacturer’s Representatives
Posted by Erin Meyer
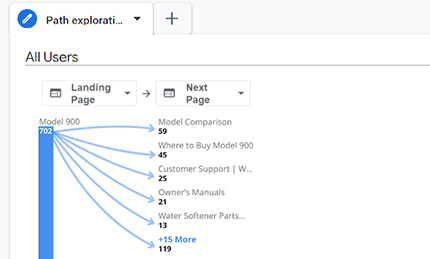
3 Actionable Reports to Improve Your Website Now
Posted by Greg Frye
Why You Should Have a Marketing Content Calendar and How to Get One
Posted by Eric Frye
Mastering Keyword Strategy to Maximize Sales
Posted by Erin Meyer
Lead Scoring: Increasing Efficiency in Your Sales Funnel
Posted by Erin Meyer